Let’s discuss the different Purposes of Wastewater Treatment Plants. More than 50 diseases spread through human excreta. Wastewater contains pathogens, helminths, worms, etc. Disposal Aspect: If wastewater is disposed of, untreated, into water bodies, it can result in the following problems. 1- Depletion of oxygen resources of streams (minimum desired DO level is 5mg/l ). 2. Cause turbidity, and colour in water bodies (aesthetically unacceptable). 3. Can be toxic to aquatic life. Reuse Aspect: Wastewater is treated to be reused for Irrigation purposes. With the growing water scarcity, the reuse aspect is gaining importance.
Wastewater Characteristics At Domestic Level
The most important first step in WWTP design. A 24-hour composite sample is essential (using an automatic sampler). Use the mean value of at least 5-10 grab samples if not possible.

Why is characterization important?
Let’s take two examples.
Table 1: Characteristics of composite raw wastewater of Nishat textile mills
| S.No | Parameter1 | N2 | Mean | PETS
(Inland waters) |
| 1 | Temperature (°C) | 14 | 38.8 | < 30 ºC |
| 2 | pH | 14 | 11.2-12 | 6-9 |
| 3 | Total solids (TS) | 14 | 4803 | – |
| 4 | Total dissolved solids (TDS) | 14 | 4671 | 3500 |
| 5 | Total suspended solids (TSS) | 14 | 187 | 200 |
| 6 | Settleable solids (SS) (mL/L) | 14 | 1.9 | – |
| 7 | Settleable solids | 14 | 102 | – |
| 8 | Chlorides (as Cl–) | 14 | 119 | 1000 |
| 9 | Phosphorous (P) | 14 | 0.7 | – |
| 10 | TKN (N) | 14 | 32 | – |
| 11 | Sulfates (as SO4-2) | 14 | 143 | 600 |
| 12 | BODT | 14 | 921 | 80 |
| 13 | BODS | 14 | 681 | – |
| 14 | CODT | 14 | 2053 | 150 |
| 15 | CODS | 14 | 1541 | – |
Impression for Wastewater of Nishat Mills
Highly alkaline. High in organic contents. Most of the organic contents are soluble (approx. 75%). The BOD: N: P is 920:32.5:0.7 or 100:3.6:0.07 (against a desirable ratio of 100:5:1 for satisfactory biological treatment). N and P are deficient in textile wastewater for satisfactory secondary/biological treatment. Therefore, the addition of N and P is required for the biological treatment of textile wastewater. Almost half of the suspended solids can settle easily in the primary sedimentation tank.
Tannery; two major processes i.e. 1- Beamhouse process( in this method in which hair and fats are removed by using lime, it has high pH) and 2- Tanyard (in this process pH is reduced up to 4, and use chromium salt to treat so it can highly stabilize and no decomposition take place here. thus Tanyard pH is low)
Table 2 Characteristics of homogenized composite raw wastewater of Saddiq leather works
| Sr No | Parameter1 | N2 | Mean | PETS
(inland water) |
| 1 | Temperature °C | 33 | 29.3 | 30 °C |
| 2 | pH | 34 | 7.55-9.66 | 6-9 |
| 3 | Total suspended solids (TSS) | 34 | 1233 | 200 |
| 4 | Settlable solids (SS) (mL/L) | 34 | 44 | – |
| 5 | Settlable solids | 28 | 942 | – |
| 6 | Chlorides (as Cl–) | 34 | 3067 | 1000 |
| 7 | Sulfates (as SO4-2) | 34 | 1240 | 600 |
| 8 | Sulfides | 34 | 156 | 1.0 |
| 9 | Chromium | 31 | 68 | 1.0 |
| 10 | BODT | 34 | 775 | 80 |
| 11 | BODS | 34 | 527 | – |
| 12 | CODT | 34 | 2442 | 150 |
| 13 | CODS | 34 | 1327 | – |
| 14 | Phosphorous (P) | 3 | 0.8 | – |
| 15 | TKN (N) | 3 | 118 | – |
Impression for Wastewater of Saddiq Leather Works
Wastewater is moderately alkaline. High in organic contents. Most of the suspended solids are easily Settleable (approx. 68%). The BOD: N: P is 775:118:0.8 (divide it by 7.75 to make it a hundred) or 100:15:0.1 (against a desirable ratio of 100:5:1 for satisfactory biological treatment). Therefore P is deficient and to be added for satisfactory biological treatment. Wastewater is high in chlorides, sulfide, and chromium. Both sulfide and chromium are toxic. (Example of Dada Tannery) Wastewater characteristics of typical domestic wastewater are given in the table below.
Table 3: Characteristics of typical domestic wastewater in the USA
| Sr No | Parameter1 | Min | Max | Typical
Value (Average) |
PETS |
| 1. | pH | 6.7 | 7.5 | 7 | 6-9 |
| 2. | TSS | 100 | 350 | 200 | 200 |
| 3. | Settleable solids (mL/L) | 5 | 20 | 10 | – |
| 4. | BOD | 100 | 300 | 210 | 80 |
| 5. | COD | 250 | 1000 | 400 | 150 |
| 6. | P | 4 | 8 | 6 | – |
7. |
TKN | 20 | 85 | 40 | – |
Impression for Wastewater of Domestic Wastewater Paksitan
Domestic wastewater can be slightly acidic or alkaline in nature. The BOD: N: P is 100:20:3 (against a desirable ratio of 100:5:1 for satisfactory biological treatment). This shows that N and P are present in sufficient amounts in domestic wastewater. 50 to 80% of organic matter is in particulate form and can be removed the at primary stage of treatment by using appropriate methods (using coagulants i.e. alum or polymers).
Flow Measurements for Wastewater Treatment Plant
Flow measurement most important record in wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) and water treatment plants (WTP). Usually, 5two devices are installed; one at the t-head and the second at the tail side. Commonly used devices are;
- Parshall flumes (mostly used for WWTPs), 2. Magnetic Flow meters (for WTPs). 3. Ultrasonic flow meters (for WTPs)
1- Parshall Flume (PF)
The Parshall flume is an affixed-dimension hydraulic structure. It is used to measure flow rate in industrial discharges, municipal sewer lines, and influent/effluent flows in water and wastewater treatment plants. The Parshall flume is used to measure flow in open channels. However, it is favored in treatment plants as a flow-measuring device. The reason is, that it lets pass a wide variety of solids such as rags, sand, and large objects that potentially will foul other flow measuring devices.
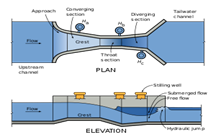
Free flow (hydraulic jump at the end of the diverging); one reading sufficient (Ha). While Submerged flow (hydraulic jump in or after throat), two readings were taken (Ha & Hb). Construction at the site or prefabricated parshall flume PF can be used. Prefebrictaed preferred (as errors occur during construction which can affect the flomeasurementet badly). Strictly follow the guidelines for accurate reading. It is suggested to select the size of PF to have free flow conditions (so we have to take only one reading and flow accuracy).
2- pH Adjustment Equalization
PH adjustment of Equalization (very important for industries otherwise it may lead to failure of the treatment). It is needed if the wastewater has extreme pH. i.e. (Very low e.g. 4- Tanyard) or (very high e.g. 12 in Beamhouse). It is essential to avoid any damage to secondary treatment. (Reason: because the bacteria work in secondary treatment (biological treatment) are very sensitive to the pH. These bacteria can survive, utilize food, and grow at neutral range).
The pH of wastewater is very low: CaO, Ca (OH) 2, (lime alkalis) or NaOH, Na2CO3 (sodium alkalis) are used. Lime alkalis are cheaper than sodium alkalis. They will increase the pH. If the pH of wastewater is very high: H2SO4, HCl, or HNO3 can be used widely. H2SO4 is used more. Equalization Basin: Equalization Basin is used where wastewater varies widely in (1)Characteristics (e.g. BOD varies first time 89mg/l second time 200mg/l) and (2) flow rate (e.g. first time 4cusec and other time 40 cusec).
It is often observed in industrial units, where different processes run in batch mode waste streams from them reach WWTP at different times. (E.g. Tanyard (pH-4) Vs. Beamhouse (pH-12) all bacteria will die in these units due to extreme pH).
Significance of Equalization in Wastewater Treatment
Equalization Basin will play its role here. It is used to (1) homogenize the wastewater and (2) provide it at a fairly constant rate to the downstream units of the wastewater treatment plant. Therefore the Benefits are;
- The performance of biological treatment is enhanced.
- Optimizes the size of the downstream treatment units.
- Minimize the neutralizing agents, thus reducing the cost of treatment.
- The life of the facilities is increased by working under constant conditions.
Detention time of Equalization Basin ranges from 4-12 hours (so water can reach here from all processes). Location: it is always placed after screening and grit chamber (very important).
(Lec-3)
WASTEWATER TREATMENT: Overview
The world disposes of 95% of the wastewater without any treatment. Only 5% of global wastewater is treated, mainly in developed countries. Wastewater treatment may be broadly categorized into three types;
- (1) primary
- (2) secondary
- (3) tertiary
- (4) sludge handling treatment.
1. Primary treatment:
Purpose:
To remove (1) floating matter, (2) inorganic fractions, and (3) large and medium-sized suspended and settleable matter from the wastewater.
Methods used:
Screens, grit chambers, and primary sedimentation tanks (primary clarifier). Total suspended solids removal TSS = 45-70% (depends on size distribution i.e. if the particle size is small then removal maybe 45%,)if the particlele size is large 70%, we will remove it. BOD removal = 25-40% (if organic matter is more in particulate matter and less in dissolved form then more removal will occur).
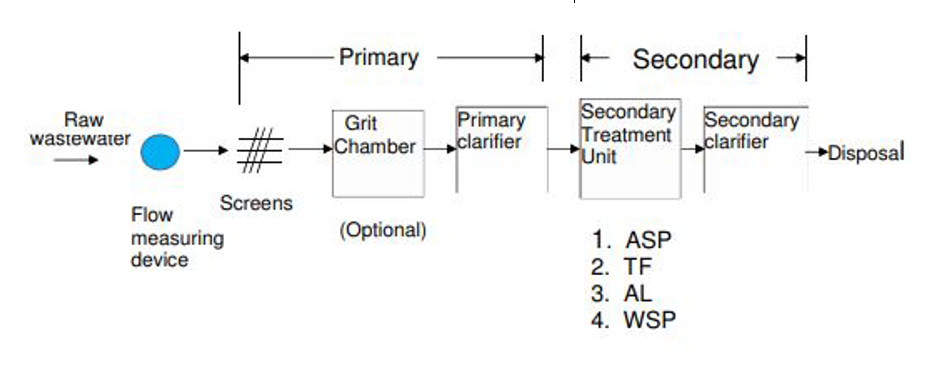
2. Secondary Treatment (Biological treatment, because the bacteria use organic matter as food)
Purpose:
Removal of soluble and colloidal (1 micrometer-10 micrometer) organic matter.
Methods used:
Activated sludge process (ASP, Trickling Filters (TF), Aerated lagoons (AL), Wastewater stabilization ponds (WSP), Rotating biological disc Contactors (RBC), Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR), Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB), Oxidation Ditch (OD), Constructed wetlands (CW), Membranebioreactorss (MBR, BOD Removal from biological treatment= 70-95%
3. Tertiary Treatment:
Purpose:
It has many applications for removing Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and all other organic and inorganic matters after primary and secondary treatment. (Why do you remove N from water? Because nitrogen exerts oxygen demand in the water body to utilize dissolved oxygen DO). Why do we remove P from water? Because P can cause Eutrophication in water bodies and excessive growth of algae).
Methods used:
We use Physical, chemical, biological, or a combination of these methods.
4. Sludge Handling and treatment
Purpose:
Reduce the sludge volume for easy handling and disposal.
Method used:
Sludge thickening, digestion, and dewatering.
Read more about wastewater treatment plants at our website – www.infinog.com